BLOCKCHAIN can be specific as a chain of blocks that contains details. The method is planned to timestamp digital files so that it’s not probable to backdate them or temper them. The idea of Blockchain is to solve the double records issue without the requirement of a central server.
The Blockchain is utilized to safely transfer products like cash, residential or commercial property, agreements, etc. without needing a third-party intermediary like a bank or government. When information is taped inside a blockchain, it is incredibly challenging to alter it.
Whats Is Blockchain? Learn Blockchain Technology
In this article, you can know about blockchain here are the details below;
The Blockchain is a software protocol same SMTP is for e-mail. Nevertheless, Blockchains could not be run without the Internet. It is likewise called meta-technology as it affects other innovations. It is comprised of severals pieces: a database, software application, some linked computers, etc.
Often the term is used for Bitcoin Blockchain or The Ethereum Blockchain, and in some cases, it’s other virtual currencies or digital tokens. However, the majority of them are discussing the distributed ledgers.
What Blockchain is NOT!
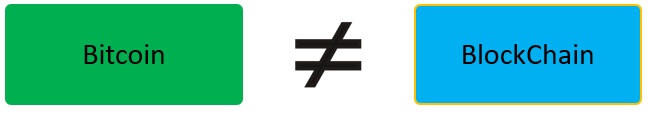
- – Blockchain is not Bitcoin. However, it is the technology behind Bitcoin
- – Bitcoin is the digital tokens, and Blockchain is the ledger to monitor who owns the digital tokens
- – You cannot have Bitcoin without Blockchain, but you can have Blockchain without Bitcoin.
Blockchain Architecture
Let’s study the Blockchain architecture by comprehending its numerous parts:
What is a Block?
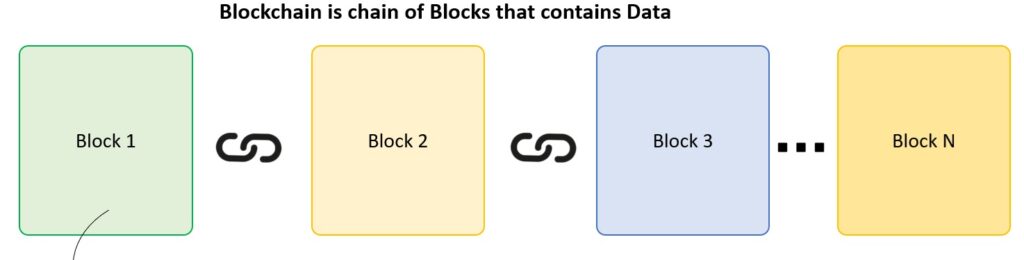
A Blockchain is a block that include information. The information which is kept inside a block depends upon the types of Blockchain. For Examples, A Bitcoin Block contains information about the Sender, Receiver, number of bitcoins to be moved. The 1st block in the chain is call the Genesis block. Every new block in the chain is link with the previous block.

Understanding SHA256 – Hash
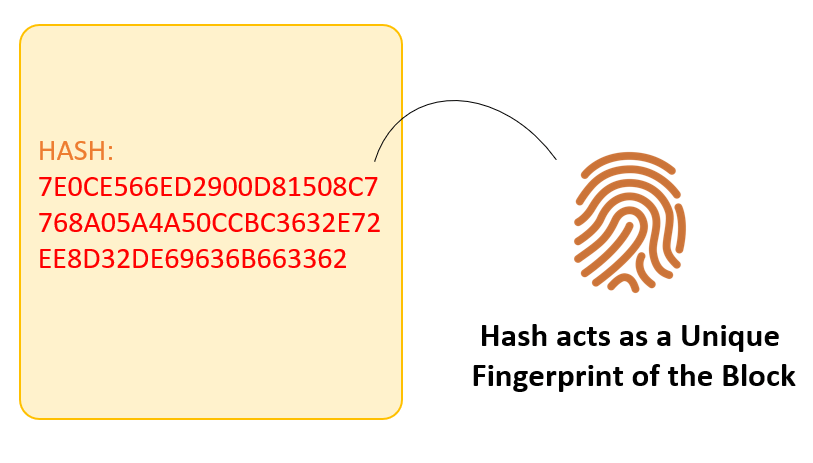
A block also has a hash. A can be comprehended as a fingerprint that is distinct to each block. It recognizes a block and all of its contents, and it’s always different, similar to a fingerprint. So once a block is produced, any modification inside the block will cause the hash to change.
Therefore, the hash is very helpful when you wish to find changes to crossways. If the fingerprints of a block changes, it does not stay the same block.
Each Block has
1. Data.
2. Hash.
3. Hash of the previous block.
Think about the following example, where we have a chain of 3 blocks. The 1st block has no predecessor. Hence, it does not consist of has the previous block. Block two consists of a hash of block 1. While block 3 includes a Hash of block 2.
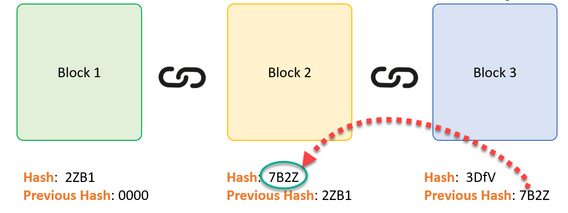
Thus, all blocks are consisting of hashes of previous blocks. This is the method that makes a blockchain so protected. Let’s see how it works -.
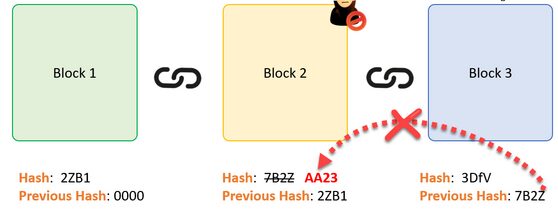
Presume an assaulter can change the data present in Block 2. The Hash of the Block likewise alters. But, Block 3 still includes the old Hash of Block 2. This makes Block 3 and all prospering blocks invalid as they do not have the proper hash of the previous block. Therefore, changing a singles block can quickly make all following blocks void.
Proof of Work.
Hashes are an excellent mechanism to prevent tampering, but computers nowadays are high-speed and can compute numerous hashes per second. In a couple of minutes, an opponent can tamper with a block, and after that, recalculate all the hashes of others blocks to make the Blockchain valid once again.
To avoid the issue, blockchains use the idea of Proof-of-Work. It is a system which decreases the development of the new blocks. A proof-of-work is a computational issue that takes a particular effort to fix. However, the time required to verify the computational problem’s outcomes is significantly less compared to the action it needs to resolve the computational issue itself.
In Bitcoin’s case, it takes practically 10 minutes to determine the required proof-of-work to add a brand-new block to the chain. Considering our examples, if a hacker would to changes data in Block 2, he would need to carry out proof of work (which would take 10 minutes) and make changes in Block 3 and all the succeeding blocks.
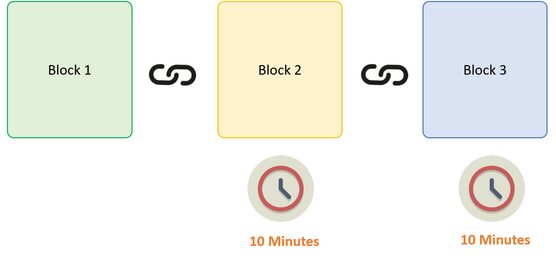
This type of system makes it quite difficult to damage the blocks, so even if you damage even a single block, you will need to recalculate the proof-of-work for all the following blocks. Hence, hashing and proof-of-work system make a blockchain protected.
Distributed P2P Network.
Nevertheless, another technique is utilized by blockchains to protect themselves, which’s by being distributed. Instead of using a central entity to manages the chain, Blockchains operate a dispersed peer-peer network, and everyone is permitted to join. When somebody enters this network, he will get a full copy of the Blockchain. Each computer system is called a node.
Let’s see what happens when any user develops a new block. This new block is sent to all the other users on the network. Each node needs to validate the block to ensure that it hasn’t been changed. After complete checking, each nodes adds this block to their Blockchain.

All these nodes in this network develop a consensus. They concur about what blocks are valid and which are not. Nodes in the systems will reject blocks that are damaged.
So, to successfully tamper with a blockchain.
1. You will require to tamper with all blocks on the chain.
2. Renovate the proof-of-work for each block.
3. Take control of higher than 50% of the peer to peer system.
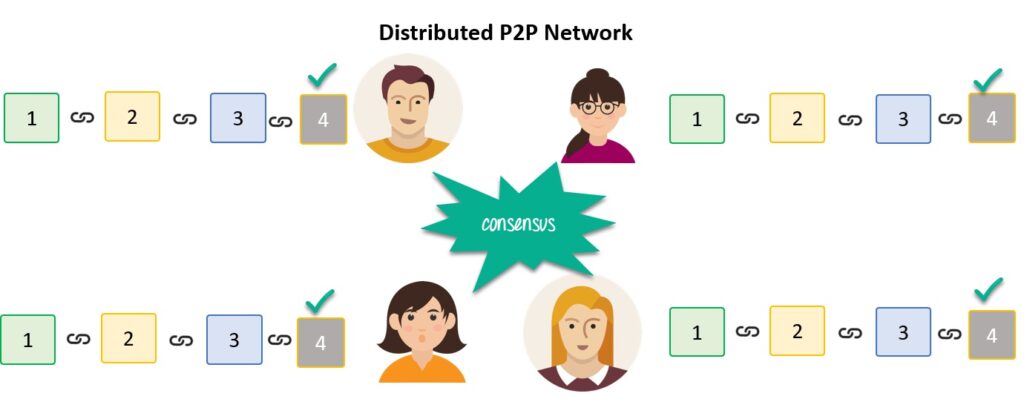
After doing all these, your tampered block becomes accepted by everybody else. This is besides an impossible job. For this reason, Blockchains are so protected.
How Blockchain Transaction Works?
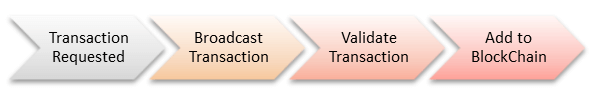
Action 1) some individual demands a transaction. The deal could be included cryptocurrency, agreements, records, or other information.
Action 2) the requested transaction is broadcasted to a P2P network with the help of nodes.
Action 3) the network of nodes validates the transaction and the user’s status with known algorithms.
Action 4) once the transaction is total, the new block is then contributed to the existing Blockchain. In such a way that is long-term and unalterable.
Why do we need Blockchain?
Here are some reasons Blockchain technology has become so popular.
Resilience: Blockchains are frequently reproduced architecture. Most nodes still operate the chain in case of a massive attack against the system.
Time reduction: Blockchain can play an essential function in the financial market by allowing the quicker settlement of trades. It does not need a prolonged verification, settlement, and clearance process because a single version of agreed-upon data of the shared journal is offered between all stack holders.
Reliability: Blockchain licenses and verifies the identities of the interested celebrations. This removes double records, reducing rates and speeds up deals.
Unchangeable transactions: By registering deals in sequential order, Blockchain licenses the unalterability of all operations, which means when any brand-new block has been contributed to the chain of journals, it can not be removed or customized.
Fraud prevention: The principles of shared details and consensus avoid possible losses due to scams or embezzlement. In logistics-based markets, Blockchain as a tracking system act to reduce costs.
Security: Attacking a traditional database is the lowering of a particular target. With the helps of Distributed Ledger Technology, each party holds a copy of the initial chain, so the system stays personnel, even the great deal of other nodes fall.
Transparency: Changes to public blockchains are openly viewable to everybody. This offers greater transparency, and all deals are immutable.
Collaboration: Allows celebrations to negotiate directly with each other without the need for mediating third parties.
Decentralized: There are requirements rules on how every node exchanges the blockchain details. This approach ensures that all transactions are validated and all legitimate transactions are included one by one.
Blockchain versions.
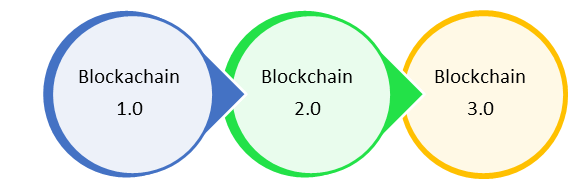
Blockchain 1.0: Currency.
The implementation of DLT (dispersed journal technology) resulted in its first and apparent application: cryptocurrencies. This permits financial transactions based upon blockchain technology. It is used in currency and payments. Bitcoin is the most famous example in this sector.
Blockchain 2.0: Smart Contracts.
The new crucial principles are Smart Contracts, small computer system programs that “live” in the Blockchain. They are complimentary computer system programs that instantly and check conditions defined earlier like facilitation, confirmation, or enforcement. It is used as a replacements for traditional agreements.
Blockchain 3.0: DApps.
DApps is an abbreviation of decentralized application. It has its backend code working on a decentralized peer to peer network. A DApplication can have frontend code and user interfaces written in any language that can telephone to its backend, like traditional Applications.
Blockchain Variants.
Public.
In this type of blockchains, ledgers are visibles to everyone on the Internet. It enables anybody to confirm and include a block of deals to the Blockchain. Public networks have incentives for individuals to sign up with and complimentary for usage. Anybody can use a public blockchain network.
Private.
The private Blockchain is within a single company. It enables only specific people of the company to validate and add transaction blocks. However, everyone on the Internet is typically allowed to see.
Consortium.
In this Blockchain variants, only a group of organizations can verify and add transactions. Here, the ledgers can be open or limited to choose groups. A consortium blockchain is used cross-organizations. Pre-authorized nodes just manage it.
Important Real-Life Use Cases of Blockchain.
1. Dubai: Smart City.
In the year 2016, the smarts Dubai office presented a Blockchain strategy. Utilizing this innovation, entrepreneurs and developers will get in touch with the financier and leading companies. The objective is to execute a blockchain base system that prefers the advancement of numerous industries to make Dubai ‘the happiest city on the planet.’
2. Incent Customer retention.
Incent is CRaaS Consumer retention as a services based on Blockchain technology. It is a commitment program which is based upon generating token for use associated with its related network. In this system, Blockchain is exchanged immediately, and it can be kept in digital portfolios of the user’s phone or accessing through the internet browser.
3. Blockchain for Humanitarian Aid.
In January 2017, the joined countries world food program began a task called humanitarian aid. The project was established in the backwoods of the Sindh area of Pakistan. By using the Blockchain innovation, beneficiaries got money, food, and all kind of deals are registered on a blockchain to guarantee security and openness of this process.
What is Cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is one cash like conventional currencies such as USD; however, it is created to exchange the digital details through a procedure made possible by certain cryptography principles. A cryptocurrency is a digital currency and is categorized as a subset of alternative currencies and virtual currencies.
Cryptocurrency is a bearer instrument based upon digital cryptography. In this types of cryptocurrency, the holder has of the currency has ownership. No other record is kept regarding the identity of the owner. In 1998, Wei Dai published “B-Money,” an anonymous, distributed electronic money system.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was launched in 2009 by an un-identified person called Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin is a Peer to Peer technology which is not governed by any central authority or banks. Presently, releasing Bitcoins and managing transactions are carried out collectively in the network. It is currently the dominant cryptocurrency of the world. It is open sources and designed for the general public, implies no one owns control of Bitcoin. There are just 21 million Bitcoins issued. Presently, Bitcoin has a market cap of $12 billion.
Anyone can utilize bitcoin without paying any procedure costs. If you are managing Bitcoin, the sender and receiver negotiate directly without using a 3rd party.
Blockchain and Bitcoin.
The Blockchain is the innovation behind Bitcoin. Bitcoin is the all digital token, and Blockchain is the ledger that tracks who owns the digital tokens. You can’t have Bitcoin without Blockchain. However, you can have Blockchain without Bitcoin.
Other prominent cryptocurrencies.
- – Ethereum.
- – Bitcoin Cash.
- – Ripple.
- – Litecoin.
Limitations of Blockchain technology.
More significant costs: Nodes look for higher rewards for finishing Transactions in an organization that works on the principle of Supply and Demand.
Slower deals: Nodes prioritize transactions with higher rewards, backlogs of transactions develop. Smaller sized ledger: It not possible to a complete copy of the Blockchain, possibly which can affect immutability, agreement, etc Deal costs, network speed: The transaction cost of Bitcoin is relatively high after being touted as ‘almost totally free’ for the very first few years.
Risk of errors: There is always a risk of mistakes, as long as the human factor is included. In case a blockchain acts as a database, all the incoming data has to be of high quality. However, social participation can quickly deal with the error.
Inefficient: Every node that runs the Blockchain needs to keep agreement across the Blockchain. This provides very low downtime and makes data stored on the Blockchain forever unchangeable. However, all this is wasteful since each node duplicates a job to reach a consensus.
Conclusion:
- – A Blockchain is a chain of blocks thats contains information.
- – The Blockchain is not Bitcoin; however, it is the innovation behind Bitcoin.
- – Every block consists of a hash.
- – Each block has a hash of the prior block.
- – Blockchain require Proof of the Work before a new block is included.
- – The blockchain database is disturbed among multiple peers and is not centralized.
- – Blockchain innovation is Resilience, Decentralize, Time minimizing, dependable, and deals with unalterable shifts.
- – Three variations of Blockchain are Blockchain 1.0: Currency, Blockchain 2.0: Smart Contracts, and Blockchain 3.0: DApps.
- – The Blockchain is Available in three various variations 1) Public 2) Private 3) Consortium.
- – Higher cost, slower deals, small ledger, the risk of error are some downsides of using this innovation.
- – Dubai- The Smarts City, Incent Customer retention, and Blockchain for Humanitarian Aid are the real-life use cases of Blockchain.
- – Bitcoin utilizes blockchain innovation, which is not governed by any central authority or banks.