Nowadays, ERP has become a familiar term to all business owners because of its importance in enhancing corporate management. ERP system has been widely adopted among different businesses from various industries. However, very few people know that this system was created and developed over a long period of time and has a significant evolutionary history.
What is ERP?
ERP or enterprise resource planning is a software or system that integrates all critical business functions such as accounting, human resources, inventory management, and purchasing, into a single system. ERPs link every part of a business. An enterprise resource planning system helps to improve a business’s performance and project management by allowing businesses to plan, budget, forecast, and accurately report on their financial health and procedures. The broad adoption of ERP systems from a long time before up to now demonstrates how critical ERP is to a successful business.
What are the ERP system’s key benefits?
ERP software solutions have brought numerous advantages for businesses as follows:
Cost savings: With ERP software’s integration and automation features, productivity and efficiency can be increased by improved inventory planning, better procurement management and better customer service.
Improve business insight: Business owners can make better decisions with a single consolidated insight report and real-time data.
Manage regulatory compliance: Track and control compliance with regulatory requirements, as well as set up warnings for non-compliance.
Mitigate and reduce risk: Core business procedures, manual chores, and reporting can all be automated. Reduce human errors and free up time and resources for employees.
Scalability: ERP systems are flexible which enables the business to scale up as the business grows with added users and processes.
Optimize customer and supplier management: ERP systems also help businesses optimize customer and supplier management by providing better access to customer and supplier information.
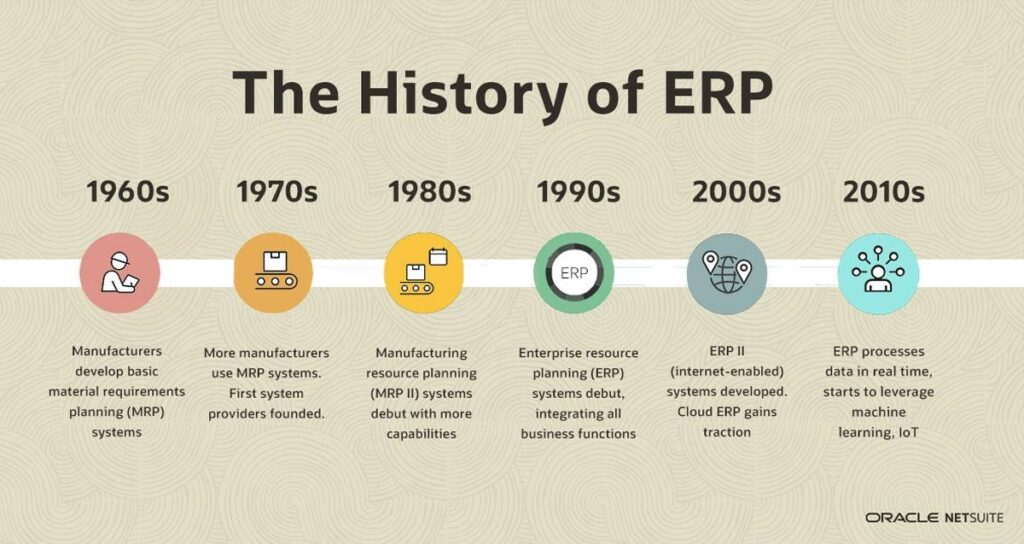
History of ERP system
The term ERP was first time mentioned in 1990 by a research firm named Gartner, to demonstrate a unified database for information from across the company. However, the enterprise resource planning system had been implemented for over 100 years in the manufacturing industry under the name MRP. Gradually, the system continues to evolve following industry and market requirements. On the other hand, ERP software during this period was installed and maintained in physical office space within a firm, and it is hosted on the company’s own computers and servers for complete control, maintenance, and ownership of the system after it is established. It is normally called on-premise ERP software.
Throughout the 1990s, ERP systems continued to evolve. The introduction of cloud ERP, which was first offered by NetSuite in 1998, was a huge milestone. Businesses could access essential corporate data via the web from any device with an internet connection with cloud ERP, which is usually seen as an upgrade over an on-premises system. Cloud solutions eliminated the need for organizations to purchase and maintain hardware, lowering the demand for IT personnel and facilitating adoption. Cloud-based ERP became popular in the mid-late 2000s and has grown in popularity in recent years.
In 2000, Gartner introduced the term ERP II to describe internet-enabled systems that can integrate with other business software solutions such as customer relationship management (CRM), eCommerce, and marketing automation, as well as back-end applications like supply chain management (SCM) and human capital management (HCM). This was a huge step forward since the more data fed into the ERP system, the easier it is to identify and handle difficulties, as well as capitalize on the potential for growth.
The coming decade is expected to bring many different changes in the market’s requirements which can lead to another evolution of ERP software to adapt to the new market needs. With the support of AI technology, ERP software would go one step further and make recommendations for improvement and optimization at every level, thus becoming the operation’s brains.
Conclusion
In general, an ERP system is frequently one of the most substantial investments that a business will have to make. It’s not only a big financial decision; it’s also a practical one that affects everything from human resources, accounting, production to marketing. Before deciding on a system, business owners should look into what’s already available and what’s coming down the pipeline in terms of ERP trends.