Gdpr principles compliance guide will be described in this article. We could all sense it coming. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which went into force on May 25, 2018, is all anyone can speak about.
You would think that five years would have been enough time for most organizations to comply, yet a lot of them haven’t. 95% of American enterprises and 81% of French businesses remained noncompliant as of 2022.
7 GDPR Principles A Guide To Compliance
In this article, you can know about Gdpr principles here are the details below;
If your organization is among those still attempting to comply, this blog will help you along the process by offering insightful information about the seven GDPR principles. Additionally, it will look at how online analytics tools may assist businesses with GDPR compliance, data protection, and improved transparency.
What is the GDPR?
The General Data & the Protection Regulation (GDPR) was created by the European Union (EU) to provide people more control over their data and to encourage openness in data processing.
The GDPR, also known by a number of other names throughout Europe (such as RGPD, DSGVO, etc.), established a set of guidelines for handling personal data of EU citizens and residents in order to ensure that organizations aren’t using user names, locations, IP addresses, information obtained from cookies, and other data carelessly.
All organizations, no matter where they are physically located, have a number of obligations to fulfill in order to comply with GDPR. Among these responsibilities are:
- Observing the rights of users
- Putting standards in place for documentation and document retention
- Making sure that data is secure
Why is GDPR compliance important?
Data is now a positively valuable resource for companies all around the world. Data is gathered and used in practically every industry. But with more people using data, there is also a greater need to safeguard people’s rights and privacy.
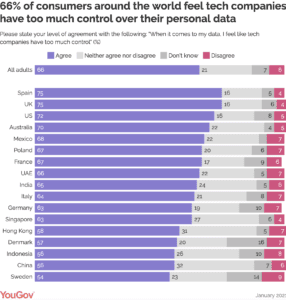
According to a YouGov survey done in 17 important markets, two out of every three adults globally think that internet companies have an excessive amount of control over their data.
The most comprehensive legislative framework, known as GDPR, was created to handle the growing concern about data handling and gathering. GDPR protects personal information against abuse, unauthorized access, and security breaches. It guarantees that companies manage data sensibly and with regard for personal privacy. It also served as a model for similar regulations in other nations, such as Sweden (54%) and Indonesia (56%), and even China, which is among the least affected regions (56%).
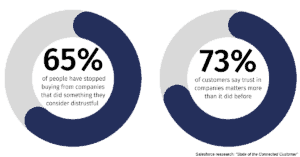
GDPR has been essential in protecting personal information and giving people greater control over it. Customer and business trust is increased by GDPR compliance. Currently, laws pertaining to privacy and data protection are in place in 71% of the world’s nations.
What are the risks of non-compliance?
The importance of GDPR has been established, but what are the ramifications and how will they affect your company? There can be serious repercussions for non-compliance, so it is not something to put off.
In the event that you violate any of the GDPR’s provisions, you may be fined up to 4% of your yearly worldwide revenue or €20 million, whichever is larger. Such large fines may be disastrous for smaller enterprises. Failure to comply may potentially give rise to legal action by private citizens or data protection agencies, resulting in additional financial damages.
Possible consequences extend beyond legal and financial domains. GDPR infractions have the potential to seriously harm your company’s reputation. If your rules and procedures are out of compliance and, consequently, do not align with potential partners, non-compliance could potentially cost you business chances. Consumers are more likely to charge businesses that take data privacy seriously than those that don’t.
Lastly, and maybe the most cowardly result of all, people can file a complaint with data protection authorities if they think you’ve violated their data rights. These complaints may start an inquiry, and if it is discovered that your company is breaching the regulations, you may be subject to all of the previously listed repercussions.
Even if you might not think it might happen to you, GDPR fines have now exceeded €4 billion in total and are rising noticeably. When comparing H1 2022 to H1 2021, fines increased by 92%. The largest fine we have witnessed to date is a record-breaking €1.2 billion assessed to Meta in 2023. However, smaller companies may also face fines. A Hungarian bank was fined €1,560 for failing to remove and amend data upon the subject’s request. (In extreme circumstances, people may also face fines. For example, a police officer fined €1,400 for utilizing official information for personal gain.)
The seven GDPR tenets and their application
By now, you need to be well-informed on GDPR, its significance, and the repercussions of noncompliance.
Finding the legal justification for each sort of personal data processing your company does should be your first step towards compliance. The next step is to assess your data processing operations to make sure they comply with the goals and tenets of the GDPR.
Article 5 of the GDPR contains seven fundamental principles that control the processing of personal data in a lawful manner:
Lawfulness, fairness and transparency
This principle guarantees that data collection and usage are done legally and openly. Customers’ consent must be obtained, and you must explain to them why you require their data. Processing of data ought to be done in an open and equitable manner.
How to abide by it
Examine your data collection procedures to determine whether and why you gather personal information from clients.
- Discover the definition of personally identifiable information (PII).
- Revise your forms and website to provide a concise and understandable explanation of why you require their data and what you plan to do with it.
- When processing an individual’s sensitive data, get their express consent.
- Include a banner asking users to consent to cookies on your website, explaining which cookies you use and why.
- The ability to build cookie consent banners and integrate with Consent Management Platforms (CMPs) to manage user consent and privacy settings is provided by website analytics solutions such as Google Analytics and Matomo.
- It is also possible to configure Matomo to disable tracking cookies, in which case the cookie consent banner would not need to be added.
- Privacy notices have to be always available.
- To make sure your cookies comply with GDPR, you need to:
- Before using any cookies, obtain permission (excluding strictly necessary cookies).
- Clearly state the purpose of each cookie and what it tracks.
- User consent should be recorded and kept on file.
- If users object to the use of specific cookies, don’t deny them access to the services.
- Simplify the process for withdrawing consent.
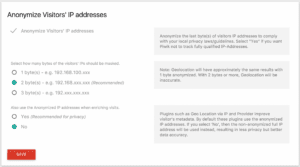
To ensure that you do not process any personal data, use tools such as Matomo, which may be programmed to automatically anonymize data.
Purpose Limitation
Only the precise, authorized uses of the data that you disclosed to your visitors, prospects, or customers at the time of collection are permitted. It cannot be used for any other purpose without my consent.
How to comply
- Clearly state the reasons behind the collection of personal information (e.g., processing orders, sending newsletters).
- Make sure you obtain the people’ express agreement before using the data for any other reason.
Data minimisation
Data minimization refers to gathering as little information as possible that is relevant to the specified goal. It is not advisable to collect or retain more data than is required. By putting data minimization procedures into place, compliance is guaranteed and data breaches are prevented.
How to comply
- Determine the bare minimum of information needed for each goal.
- To find and remove sites of data gathering that are not necessary, conduct a data audit.
- Avoid requesting information that isn’t necessary or storing data that isn’t necessary for running your company.
- When data is no longer needed, remove it by putting data retention policies into place.
Accuracy
It is your responsibility to hold current & accurate data at all times. If you have inaccurate information for your clients, you should have procedures in place to quickly remove or update any data.
How to comply
- Establish a procedure for updating and reviewing client data on a regular basis.
- Give clients a simple mechanism to ask for data corrections if they discover any mistakes.
Storage Limitation
Data shouldn’t be preserved for longer than is required. Only keep it for as long as you have a good cause to, which should be the intended use that was agreed upon. Data should be securely disposed of when it is no longer required. The amount of time that data can be stored is unlimited.
How to comply
- Establish precise timeframes for the various categories of data you gather.
- Create policies for data retention and follow them religiously.
- When data is no longer required for the reasons you indicated, delete it.
Integrity and confidentiality
Data must be secured and locked away, among other precautions, to prevent unauthorized or illegal access.
How to comply
- Maintain access controls and encryption to securely store personal data, and store it within the EU or another region with comparable privacy laws.
- Provide data protection training to your employees and limit data access to those who require it for work-related purposes.
- Regularly evaluate security and take immediate action to fix issues.
Accountability
Being accountable entails taking ownership of upholding the other values. You have to show that you are abiding by the regulations and that data privacy is important to you.
How to comply
- Name a person in charge of data privacy in your organization, such as a Data Protection Officer (DPO).
- Keep thorough records of all data processing operations, including any breaches.
- Reports of data breaches have to be made within 72 hours.
Maintaining compliance with GDPR requires constant examination and updating of your processes.
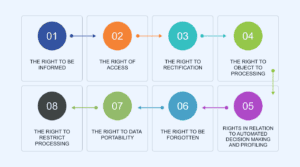
What are GDPR rights?
The GDPR grants individuals a digit of rights. They have more control over their personal data thanks to these rights.
The right to information: People have the right to know why their data is needed.
What to do: Describe the need for and intended use of personal data.
The right of access: Anyone can ask to see the personal information you have on them.
What to do: Within a month of receiving a request, provide a free copy of the data.
The right to rectification: Your clients have the right to request that you fix any data flaws or inaccuracies that they discover.
What to do: Immediately edit any inaccurate information to make sure it is current and accurate.
Customers have the right to object to the processing of personal data where it is being used for certain objectives, such as direct marketing.
What to do: If you have a good cause to process the data, then honor this objection.
Rights about automated decision-making and profiling: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) grants people the right to object to decisions that are made only on the basis of automated processing, including profiling, if doing so will materially affect them.
What to do: In such circumstances, grant people the right to human intervention and allow them to voice their opinions.
The right to be forgotten: People have the ability to ask for the erasure of their personal information in specific situations, such as when it is no longer required or they withdraw their consent.
What to do: Unless you are required by law to retain the data, comply with such requests.
The due to data portability allows someones to obtain their personal information in a format that is widely used and machine-readable.
What to do: Give the person the data if they wish to move it to a different service provider.
Right to restrict processing: Clients may request that you, among other reasons, temporarily cease processing personal data while they challenge its correctness or object to its use.
What to do: Don’t analyze the data any further; instead, store it for the duration.
Are all website analytics tools GDPR compliant?
Sadly, not every online analytics tool is created equal. Anywhere in the globe that you process the personal data of residents or citizens of Europe, you are required under GDPR to comply with certain requirements.
Even if your online analytics tool gives you useful information into your user base and website traffic, not all of them are GDPR compliant. Regardless of your best efforts to follow the seven principles and your rights under the GDPR, you will never be completely compliant if you use a non-compliant tool.
When working with data and utilizing tools for website analytics, keep the following in mind:
Collection of data
In accordance with the lawfulness, fairness, and transparency concept, unless you completely anonymize data with Matomo, you must obtain users’ agreement for tracking if you are utilizing website analytics tools to gather visitor behavioral data.
You should also be transparent about the kinds of data you gather, including IP addresses, device details, and browsing habits. Keep in mind that data collecting attempts to enhance the functionality of your website and gain a deeper understanding of your audience.
Storage of Data
Assure your visitors that you adhere to the GDPR’s storage limitation principle and that you only retain personal data for as long as is necessary. Indicate in detail the length of time that certain data kinds must be retained, as well as when the data will be erased or anonymized.
Usage of data
Make it clear that the information you gather will only be used for website analytics and for no other reason in order to adhere to the purpose limitation principle. Additionally, you should swear that you won’t give them express approval to share their information with third parties for marketing purposes or unrelated uses.
Anonymisation and Pseudonymisation
GA4 (Google Analytics) and Matomo both have privacy-protecting features including IP anonymization. Explain how you utilize these technologies and add that, in order to better protect personal information, you may choose to employ unique IDs or pseudonyms in place of real names.
Cookies and consent
Advise visitors that cookies and other tracking technologies are used on your website for analytics. In addition to cookieless choices that do not require consent banners, Matomo gives users the ability to customize cookie banners and opt-out options so they can set their preferences about cookies and tracking.
Right to access and correct data
Advise guests of their rights and how to make an information request. Tell them how to change their choices and fix errors in their data.
Security measures
Reassure guests that you have taken appropriate steps to protect their data from unauthorised entrance and breaches and that you take data security seriously. This is also your chance to showcase any access controls or encryption you employ to protect data.
Contact information
Give consumers the information to get in touch with your company’s Data Protection Officer (DPO) if they have any issues or concerns about their privacy or data.
Think about how well web analytics solutions comply with GDPR regulations before making your choice. Look for characteristics like data storage inside the EU or another jurisdiction with comparable privacy laws, data retention limitations, anonymization, consent management alternatives, and security measures.
Matomo provides a sophisticated GDPR manager. By offering users the option to access, withdraw consent, object, or remove their data in addition to the anonymizing capabilities, this ensures that websites are entirely compliant with GDPR.
Lastly, adopting Matomo gives you complete control over your data, which is hosted on your own servers with Matomo On-Premise or with us in the EU if you’re using Matomo Cloud. This allows you to be data-driven while yet adhering to international privacy regulations. We are also trusted across sectors because we offer precise data—no artificial intelligence is used to fill in the blanks—a strong API that enables you to integrate your data with other tools, and cookieless tracking choices that eliminate the need for cookie consent banners. Furthermore, you may examine the internal mechanisms thanks to our open-source nature, which provides direct evidence of security.
Ready to become GDPR compliant?
Achieving GDPR compliance is crucial for any firm, big or small, that handles data belonging to citizens or residents of the EU. You don’t have to spend a lot of money or five years to get compliant. You can quickly become compliant with privacy regulations and save costly fines and reputational harm by using the appropriate procedures and tools.
Being GDPR compliant doesn’t have to mean sacrificing insightful data. An ethical substitute for Google Analytics is Matomo, which does not exploit data for its “own purposes.” When you use our all-in-one web analytics platform, you always and completely own your data.